|
SHJH hr 小鼠的心脏衰老表型研究
|
刘荣乐 1, 程灏 1, 尚付生 2, 常书福 1(  )(  ), 徐平 3
|
|
Study on Cardiac Aging Phenotypes of SHJH hr Mice
|
LIU Rongle 1, CHENG Hao 1, SHANG Fusheng 2, CHANG Shufu 1(  )(  ), XU Ping 3
|
|
|
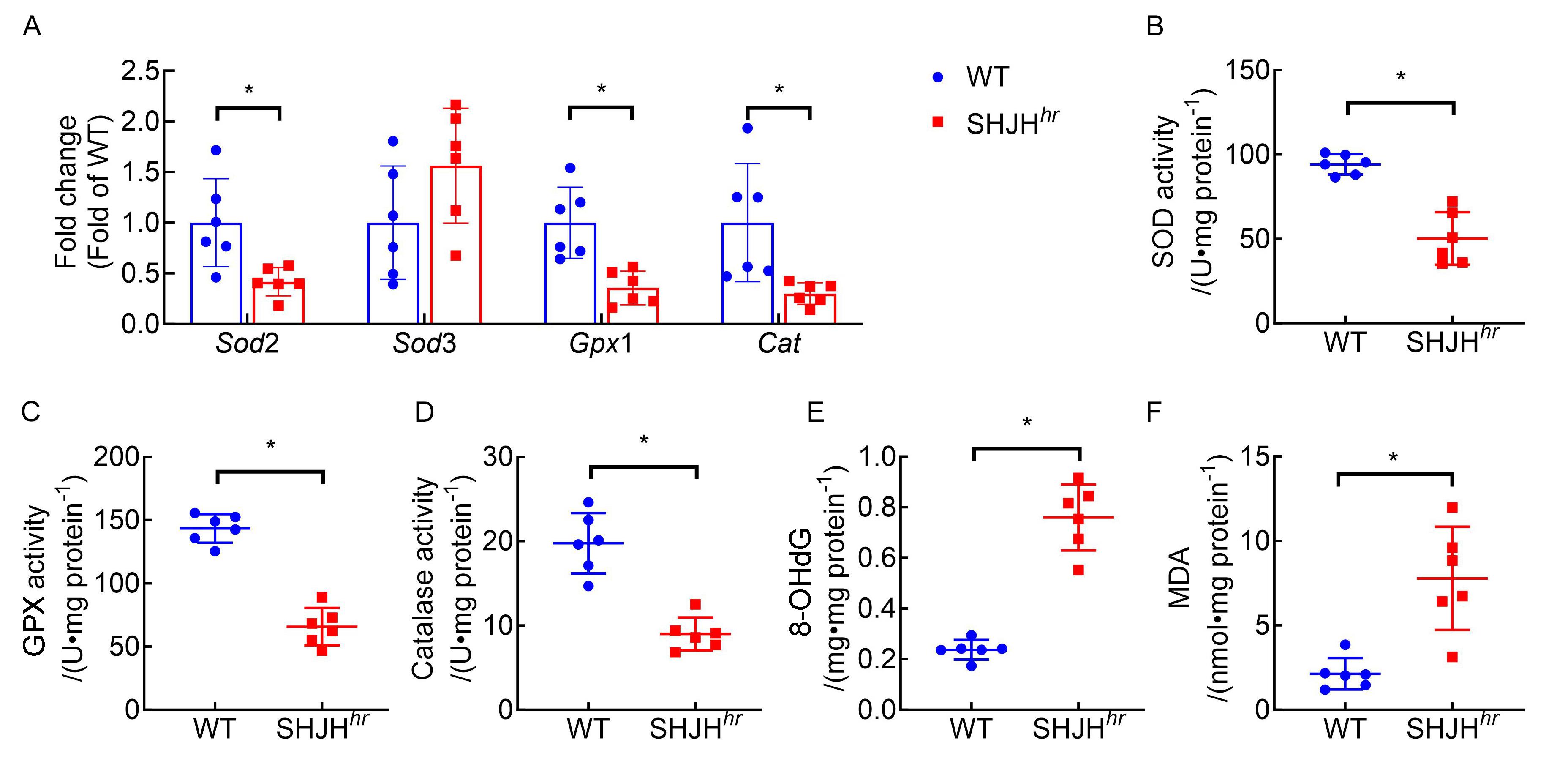
图4. 24周龄SHJH hr 小鼠的心脏组织氧化损伤相关因子分析
注:A,RT-PCR检测氧化应激因子超氧化物歧化酶(Sod)2、Sod3、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(Gpx)1和过氧化氢酶(Cat)的mRNA表达水平;B~D,ELISA法检测SOD、GPX和 CAT活性; E,ELISA法检测8-羟基-2'-脱氧鸟苷(8-OHdG)含量表达;F,ELISA法检测丙二醛(MDA)水平。以非早衰的野生型ICR小鼠(WT组)作为对照,n=6,与WT组比较,*P <0.05。
|
Figure 4. Analysis of oxidative damage-related factors in cardiac tissue of 24-week-old SHJH hr mice
Note: A, RT-PCR was used to measure the mRNA expression levels ofoxidative stress factors superoxide dismutase(Sod)2, Sod3, glutathione peroxidase(Gpx)1, and catalase(Cat); B to D, ELISA was used to determine the activities of SOD, GPX, and CAT; E, ELISA was used to measure the expression level of 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG); F, ELISA was used to assess the level of malondialdehyde (MDA). Wild-type ICR mice without premature aging (WT group) were used as controls, n=6. Compared with the WT group, *P <0.05.
|
|
 |
|
|

